Discover the power of health data in concrete examples that increase efficiency, reduce costs and fraud, and improve the doctor-patient experience.
Big Data continues to change the approach of the most diverse fields, from sales to human resources and also medicine and health care. The amount of data accumulated by the different sectors of medicine is very extensive, from electronic health records of diseases and their causes, patient portals, payer records, medical staff schedules, and web search engines, among others.
Let’s look at some examples and trends of the potential of data in the health area.
In recent years, machine learning applied to health records has been key in dealing with an event that shocked the world: the COVID-19 pandemic. The analysis of large volumes of data made it possible, for example, to obtain information on monitoring, detection, diagnosis, and treatment of diseases associated with the virus and on the characteristics of patients with prolonged COVID.
“According to a survey, 88% of people were willing to use wearable technology to measure and track their vital signs, and 47 % of chronic disease patients and 37% of non-chronic disease patients consider sharing their health information. health with research organization Source: National Library of Medicine”
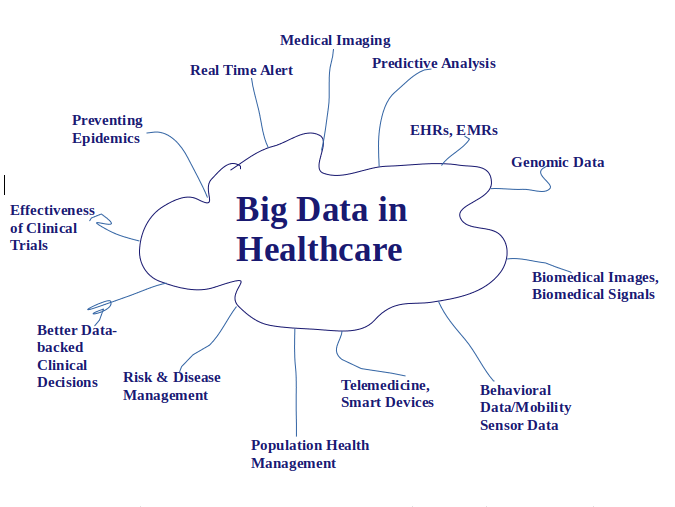
Use cases of Big Data in health:
The health sector is changing very quickly thanks to the engine of transformation. Technology, innovations, and the use of data have benefits for patients, doctors, and the ecosystem in general.
Here are 4 use cases:
- Predictive analysis that allows early diagnosis and greater personalization in treatments: the results improve when the volume of information that can be gathered about each patient is also known to take advantage of, achieving a 360 view of it.In addition to the level of detail that new data discovery techniques allow to achieve, one must take into account the potential for the exchange of patient information between clinical centers around the world. Additionally, they speed up diagnosis, make it possible to optimize patient outcomes, and reduce costs.
- Fraud Reduction and Abuse Prevention – The cost of fraud, waste, and abuse in the healthcare industry is a key factor in the expansion of healthcare costs in many countries. The use of Big Data makes it possible to prevent this type of situation and avoid them before they have consequences.For example, through a predictive modeling environment, it is possible to identify abusive and unjustified claims. The key is the ability to store records and go back in history to analyze large unstructured data sets.
This perspective of the claims history worked with automatic learning algorithms, allows the detection of anomalies and patterns, based on factors that may seem improbable, from the detection of identical prescriptions for the same patient to the overuse of services in short periods of time.
“95 % of identity theft comes from stolen medical records. In 2021, healthcare data breaches cost companies an average of $9.3 million per incident. Source: Tech Jury“
- Real-time patient monitoring: it is the basis for carrying out more proactive care. The real-time analytics capability will serve to send alerts to care providers so they are immediately aware of changes in a patient’s condition and identify larger population trends to develop better treatment plans. Avoiding latencies in health issues can provide physicians with information that helps them make decisions more efficiently, thus saving lives and planning more effective interventions.
- Smart Staffing and Personnel Management: Optimizing the activities and time of medical staff through performance analysis in a large number of key areas, will enable better distribution of tasks and quality care for patients. The imbalance in the administration of human resources leads to saturation or lack of personnel, which can generate risks of lower motivation for work and increase discontent.
Sensors and portable devices, cognitive computing solutions, and new data storage and processing systems are the pillars on which the industry continues to advance along the path that marks innovation and effective data management, making available to professionals and patients countless benefits.