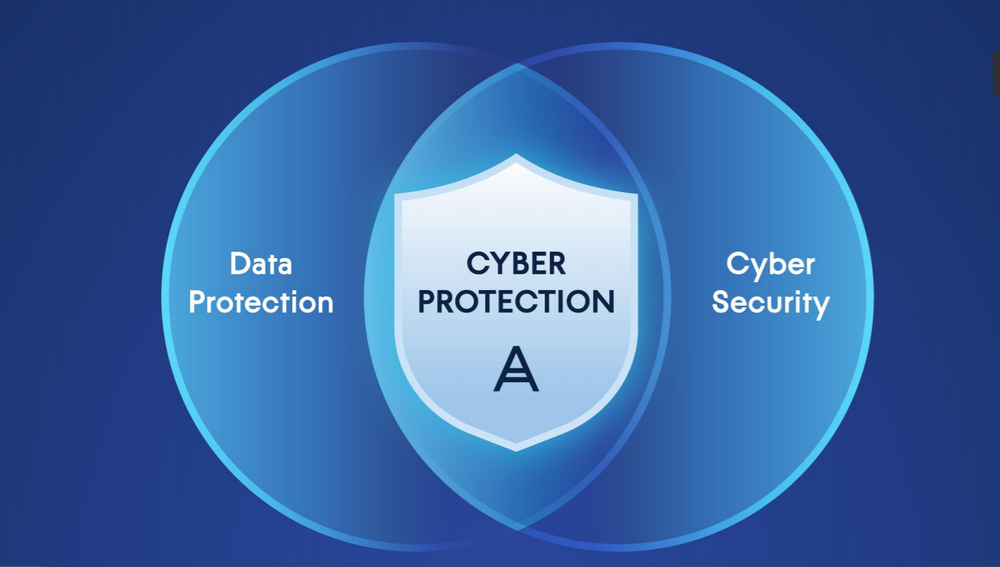
Cyber protection is the integration of data protection and cyber security, a necessity for secure business operations in today’s cyber threat landscape.
“This image shows the relationship between cyber protection, data protection, and Cyber Security. Cyber Security and Data Protection are a part of an all-in-one Cyber Protection solution”
In the modern world, businesses face a variety of threats to digital data and operations. These risks can be internal, caused by employees or contractors, or external, caused by cybercriminals, nation-states, or even your own customers.
They can be deliberate acts of espionage, disruption, or theft, or accidental acts of negligence and human error.
Regardless of the vector or motivation, cyber threats can be absolutely devastating to organizations and the people they employ and serve.
It’s fair to say that data is now the world’s most valuable resource. They are at the core of almost all business operations and decision-making.
And data growth is explosive, doubling in volume every two years. Effective cyber protection is increasingly necessary to safeguard organizations, people, and our society in general.
How is cyber protection different from cyber security?
Cyber security is the practice of defending your networks, systems, and applications from cyber-attacks. Types of cyber security include but are not limited to:
- Network Security – Protecting internal networks from unauthorized access, with tools like remote access management and Two-Factor Authentication (2FA).
- Application Security – Prevents data and code for business-critical software (both in use and in development) from being stolen or hijacked, such as with encryption and penetration testing.
- User education: Teach employees and customers best practices to avoid cyber threats, such as malware and phishing attacks.
Where cyber security and cyber protection differ is in their relationship to data. Cyber security is not focused on data protection itself, but on protecting the systems that make data access, storage, transfer, and authentication possible.
If bypassed or disabled by unknown threats, cybersecurity solutions can’t do much to help you restore data and systems in a timely manner.
Cybersecurity is naturally an important part of staying protected online, but modern challenges in data protection have made this approach insufficient on its own, especially with an organization’s livelihood at stake.
Rather, cybersecurity must be integrated with data protection to cover workloads and address new forms of malicious cyberattacks more comprehensively.
What cyber protection problems do companies face?
The potential for data loss, leakage, corruption, tampering, and theft has never been higher. Data is increasingly at the heart of daily business operations, and companies are generating staggering volumes, much of which is highly sensitive and may contain personally identifiable information about customers and employees.
“Increase in cyber threats during 2022”
Meanwhile, cybercriminals are using automation to create and iterate new cyber threats with blazing speed.
They are even customizing their attacks with information gleaned from corporate websites and social media, piquing the curiosity of their targets, and enticing them to cast aside their better judgment and open questionable hyperlinks or email attachments.
Protecting business-critical data is key but doing so is a significant undertaking. Organizations face three main problems in managing their digital operations:
Security
Cyber threats already pose a huge challenge to businesses, and as operations continue to shift to digital models, there are signs that these threats will continue to increase.
Ransomware alone is responsible for tens of billions of dollars in damage each year around the world. That growth is fueled by tech-savvy cybercriminals.
The same cutting-edge technologies used by legitimate companies are also being exploited by criminal gangs and even rogue nations.
Harnessing artificial intelligence and vast amounts of computing power, malicious actors are industrializing their malware capabilities, outperforming many traditional anti-malware solutions, and making zero-day attacks more damaging.
Cybercriminals operate with a wide and growing variety of tactics. Some will attempt to lock down data and demand a ransom for its restoration, and will increasingly exfiltrate sensitive information for public disclosure if their demands are not met.
Others point to weaknesses in regular business processes to disrupt services or discreetly divert funds. They can target their software vendors, hoping to compromise dozens of downstream companies in one fell swoop.
They will often seek out data backups directly to increase the impact of their attacks and the influence they have on victims.
In this evolving threat landscape, businesses need cyber protection solutions that can safeguard large stores of critical data in increasingly complex infrastructures, while keeping up with ever-changing threats, and that can verify the authenticity of their Backups.
Complexity
Between mobile devices and the Internet of Things (IoT), computing is getting closer to the point of origin of data. Businesses demand lower latency, faster response times, and continuous service availability, even with intermittent connectivity.
Soon, as few as 1% of devices will be in actual data centers, while smart devices, home automation systems, and wearable devices take care of a larger share of processing needs.
But while decentralization enables these in-demand benefits, it also adds incredible complexity to the task of data protection.
Instead of managing and protecting a centralized data center, with standardized and familiar equipment, IT professionals must now find a way to protect all the devices and endpoints that access and store their company data.
If they don’t, a successful cyberattack against another brand’s Internet-connected refrigerator could put their operations at risk.
Cyber protection cost
Between the global shift to online operations and the need to safeguard colossal data stores on a wide variety of devices, the attack surface for cyber threats is larger than ever.
Effective cyber protection of business-critical data requires many different capabilities. Some companies use different solutions for each of these needs: one product for antivirus, another for data backup, and perhaps some paid plugins for patch management or URL filtering.
But covering all the risk factors can be expensive, and this complex web of multiple products is itself a risk factor.
As more and more solutions are added to an organization’s protection plan, technicians must spend an increasing amount of time just staying on top of what is and isn’t protected.
Finding products that protect your entire attack surface can be tricky, especially if you have multiple types of hardware and operating systems to protect, and newly installed updates to one solution can introduce incompatibilities with others.
When a business must spend too much time and energy managing its security solutions, it’s not getting the full value or effectiveness of the protection it paid for.
What are the five vectors of cyber protection?
It’s clear that in the modern cyber threat landscape, businesses need solutions that provide more than just data backup or antivirus protection.
They need data to be available anytime, anywhere. They need to control who can see and access that data, keeping sensitive information out of the wrong hands.
They need it to be protected against cyber threats and against natural disasters or other events that could cause data loss and disrupt business continuity.
And when restoring data from backups, businesses need to know that it hasn’t been modified or corrupted by nefarious actors.
“Five Vectors of Cyber Protection – Safety, Accessibility, Privacy, Authenticity, Security”
To meet these needs, Acronis develops solutions that address the five cyber protection vectors, also known by the acronym SAPAS:
- Security: Ensuring that a reliable copy of your data is always available.
- Accessibility: Ensuring that data is available from any physical location, at any time.
- Privacy: Ensuring full control and transparency over who can see and access your data.
- Authenticity: Ensuring that the backed-up data is an exact and unaltered replica of the original data.
- Security: Ensuring that data, applications, and systems are protected from cyber threats.
Meeting all five vectors of cyber protection is technically possible with disparate solutions, but this approach tends to be costly and difficult to manage.
Relying on separate tools for needs like backup, antimalware (early launch anti malware), remote management, and disaster recovery requires IT technicians to learn and maintain each of these solutions.
Enterprises with multiple types of devices and operating systems to protect can struggle to keep capabilities aligned, creating gaps in workload protection.
And having multiple agents running can overload systems, while each product update threatens to cause incompatibilities.